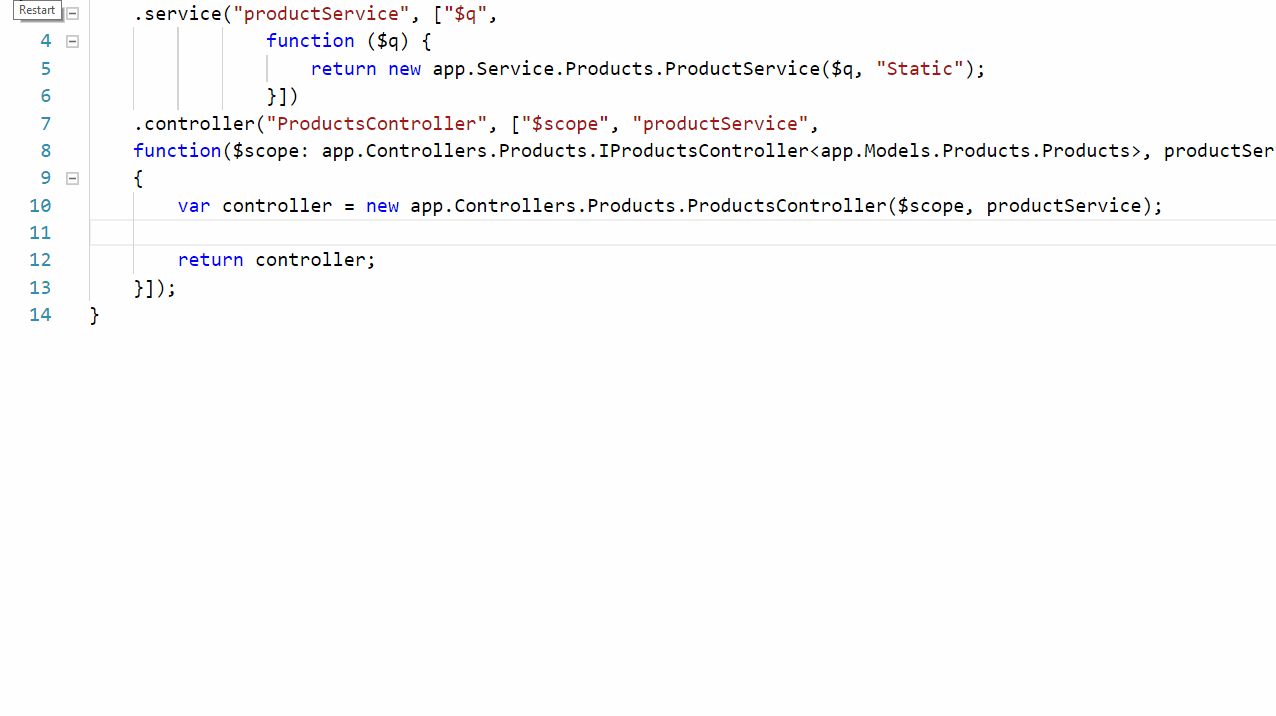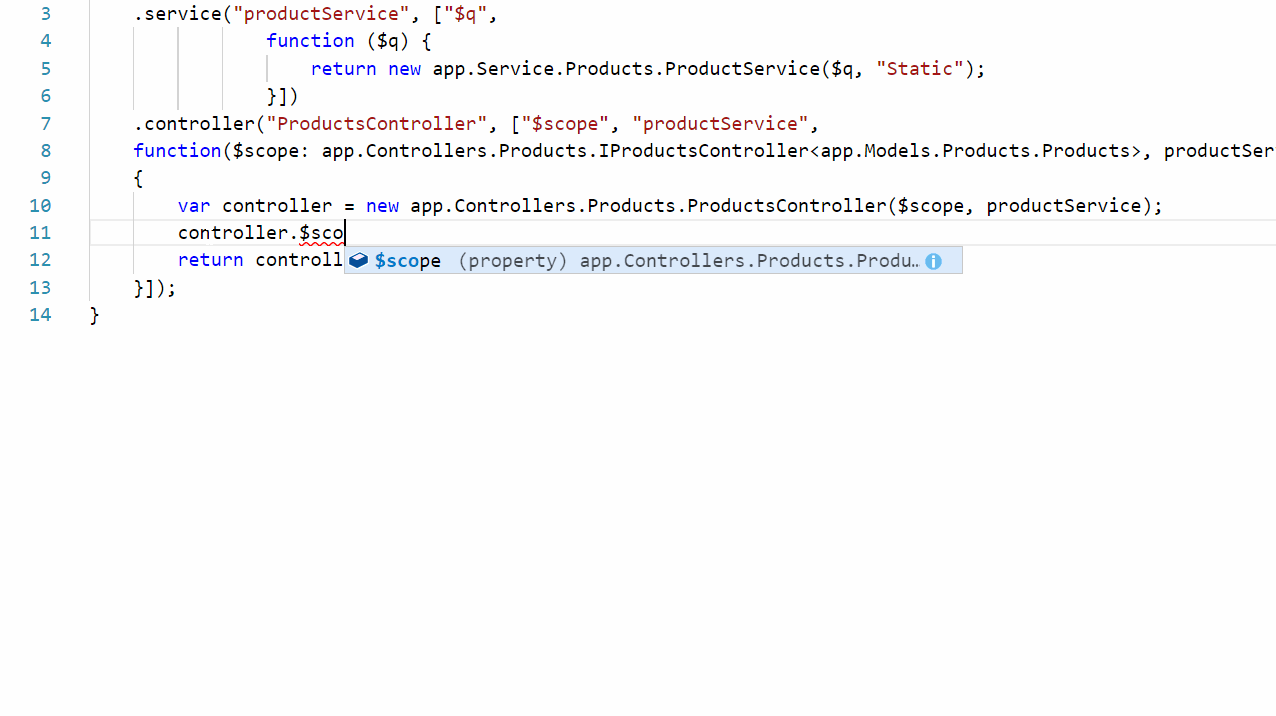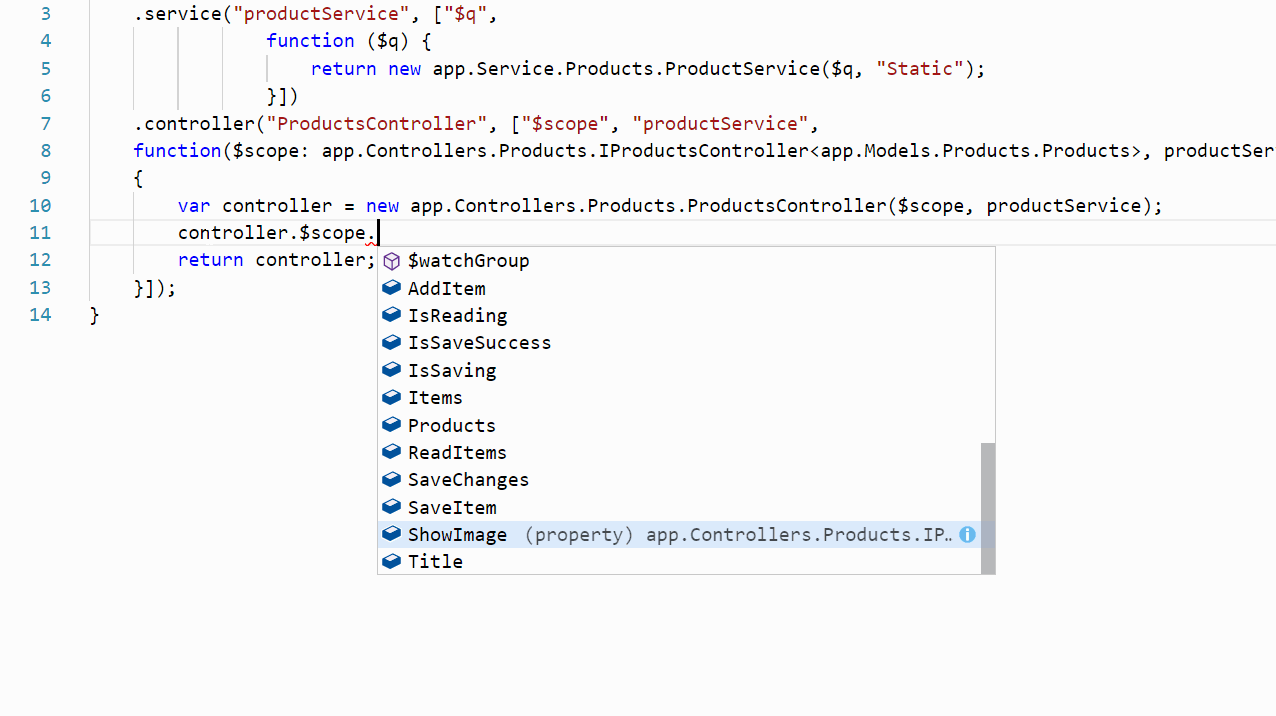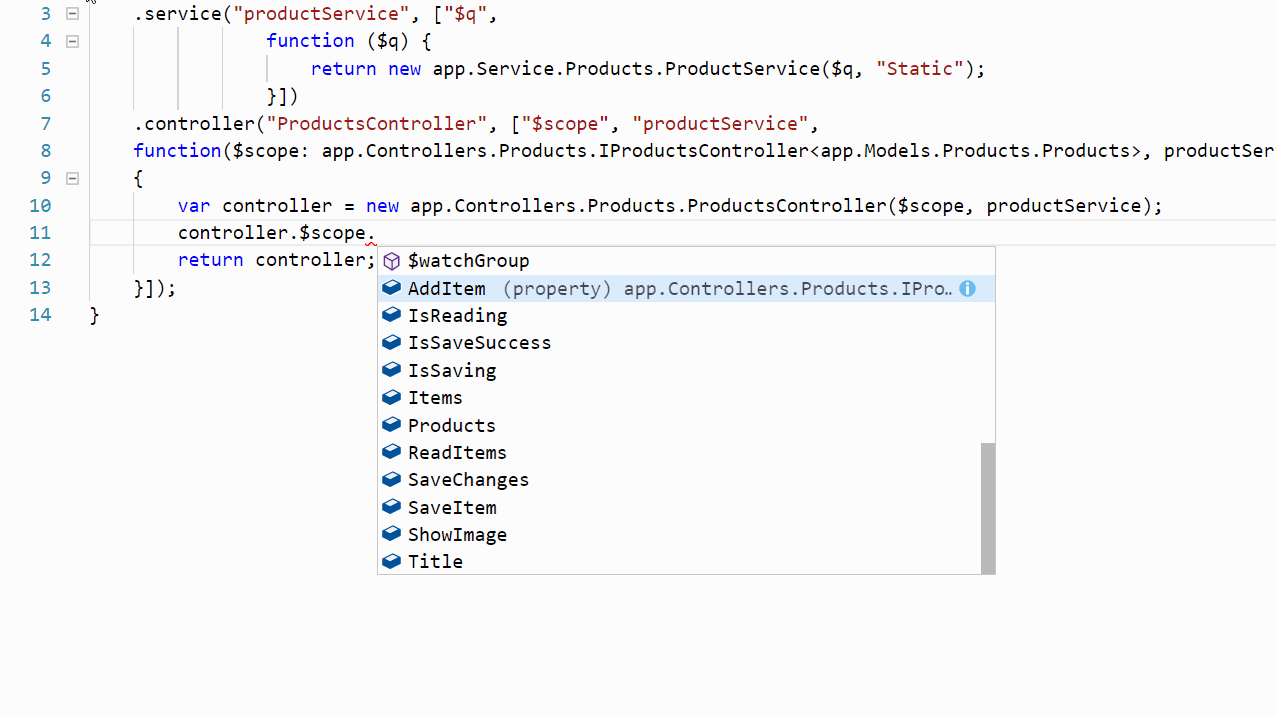
In this blog, we are going to see how to create a AngularJS service that will make use of the $q service for performing asynchronous processing. The $q service of AngularJS. You can find the $q documentation here. I have used TypeScript for scripting the classes as its been a blessing for a C# developers like me.
The scenario for this service will be, Products Service will call an external business service to get the data. The business service is developed by an external team which is not ready during the UI development. I hope most of us might have encountered such scenario and one of the ways to deal with such scenarios is to create a stub. I am going to use Repository Pattern that will intern call static or service repository based on condition.
The following is the class diagram of the classes and interfaces involved and a short note below provides a short description about it

Repository pattern for getting data from service or static repository
IRepositoryManagerBase:
This interface provides the implementation for creating a repository manager class. This is a generic interface the takes any type as the parameter. The method GetRepository will be used to load the repositories based on the criteria passed. Will explain more about it in ProductsRepositoryManager class.
export interface IRepositoryManagerBase
{
GetRepository(repositoryType: string): IRepository;
RepositoryType: string;
Repository: IRepository;
}
IRepository:
Interface used to provide CRUD operation on repository classes like GetAll, GetbyId, SaveItem, DeleteItem, AddItem, DeleteAll, SaveItems, AddItems and DeleteItems. The important one to understand here is that all the method returns promise.
export interface IRepository{
GetAll(): ng.IPromise<Array>;
GetbyId(id: number): ng.IPromise;
SaveItem(item: TEntity): ng.IPromise;
DeleteItem(item: TEntity): ng.IPromise;
AddItem(item: TEntity): ng.IPromise;
DeleteAll(): ng.IPromise;
SaveItems(items: Array): ng.IPromise;
AddItems(items: Array): ng.IPromise;
DeleteItems(items: Array): ng.IPromise;
}
IProductRepository:
This interface extends the IRepository interface and has specialization method specific to Product
export interface IProductRepository extends IRepository{
GetByName(name: string): ng.IPromise<Array>;
GetByCode(code: string): ng.IPromise<Array>;
GetByCategory(category: string): ng.IPromise<Array>;
}
Handling Asynchronous calls with AngularJS $q service
ProductServiceRepository:
This repository class extends IProductRepository interface that used to get the data from an external service and as of now I will give the skeleton of how to implement the deferred pattern all the methods. This can be considered as a boilerplate code and can used in any AngularJS.
export class ProductServiceRepository implements IProductRepository<Models.Products.Products>{
static $inject = ["$q"];
constructor(private $q: ng.IQService) {
}
public GetAll(): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetbyId(id: number): ng.IPromise<Models.Products.Products>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByName(name: string): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByCode(code: string): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByCategory(category: string): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public SaveItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public DeleteItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public AddItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public DeleteAll(): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public SaveItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public AddItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public DeleteItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
// Call to external service here
d.resolve();
}
catch (e) {
// Code to get the error from service here
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
}
ProductStaticRepository:
This repository class extends IProductRepository interface that used to populate the required inside very method and store in a collection. This method also uses deferred pattern all the methods. This method will come handy until the Business Service is made ready.
export class ProductStaticRepository implements IProductRepository<Models.Products.Products>{
static $inject = ["$q"];
private result: Array<Models.Products.Products> = new Array<Models.Products.Products>();
constructor(private $q: ng.IQService) {
}
public GetAll(): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
try {
this.result = new Array<Models.Products.Products>();
for(var counter:number = 0; counter < 10; counter++){
var item = new Models.Products.Products(
counter + 1,
"ProductName " + (counter+1).toString(),
"PROD" + (counter+1).toString(),
new Date(),
"Product" + (counter+1).toString() + "-Description",
(counter+1)*1000,
"ImageUrl00"+ (counter+1).toString(), (counter%2 == 0) ? "Toys": "Books");
this.result.push(item);
}
d.resolve(this.result);
}
catch (e) {
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetbyId(id: number): ng.IPromise<Models.Products.Products>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
var result: Models.Products.Products;
try {
for(var item in this.result){
result = this.result[item];
if(result.ProductId == id)
{
break;
}
}
d.resolve(result);
}
catch (e) {
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByName(name: string): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
var results: Array<Models.Products.Products>;
try {
var currentitem: Models.Products.Products;
for(var item in this.result){
currentitem = this.result[item];
if(currentitem.ProductName == name)
{
results.push(currentitem);
}
}
d.resolve(results);
}
catch (e) {
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByCode(code: string): ng.IPromise<Array<Models.Products.Products>>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
var results: Array<Models.Products.Products>;
try {
var currentitem: Models.Products.Products;
for(var item in this.result){
currentitem = this.result[item];
if(currentitem.ProductCode == code)
{
results.push(currentitem);
}
}
d.resolve(results);
}
catch (e) {
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public GetByCategory(category: string): ng.IPromise<Models.Products.Products[]>{
var d = this.$q.defer();
var results: Array<Models.Products.Products>;
try {
var currentitem: Models.Products.Products;
for(var item in this.result){
currentitem = this.result[item];
if(currentitem.ProductCategory == category)
{
results.push(currentitem);
}
}
d.resolve(results);
}
catch (e) {
// $.Deferred<Models.Products.Products[]>().reject(e);
d.reject(e);
}
return d.promise;
}
public SaveItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public DeleteItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public AddItem(item: Models.Products.Products): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public DeleteAll(): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public SaveItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public AddItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
public DeleteItems(item: Array<Models.Products.Products>): ng.IPromise<boolean>{
...
}
}
ProductRepositoryManager:
This class is repository manager class that provides the repository class based on the string parameter passed to the GetRepository(repositoryType: string). If the parameter is passed as “Static” then an instance of ProductStaticRepository is returned or when “Service” is passed as parameter then ProductServiceRepository is returned.
export class ProductRepositoryManager implements IRepositoryManagerBase<Models.Products.Products>{
private repoType: string;
private _repository: IRepository<Models.Products.Products>;
constructor(repositoryType: string, private $q: ng.IQService){
this.repoType = repositoryType;
this._repository = this.GetRepository(this.repoType);
}
public GetRepository(repositoryType: string) : IRepository<Models.Products.Products>{
this.repoType = repositoryType;
var itemToReturn:IRepository<Models.Products.Products>;
switch(repositoryType){
case "Static":
itemToReturn = new ProductStaticRepository(this.$q);
break;
case "Service":
itemToReturn = new ProductServiceRepository(this.$q);
break;
case "Others":
default:
itemToReturn = null;
break;
}
return itemToReturn;
}
public get Repository(): IRepository<Models.Products.Products>{
return this._repository;
}
public get RepositoryType(): string{
return this.repoType;
}
public set RepositoryType(value: string){
this.repoType = value;
}
}
Product Service
This is the AngularJS service that is derived from the IRepositoryManagerBase class and this will create an instance of ProductServiceRepository/ProductStaticRepository repository class based on the criteria. Some important explanation on the implementation in the ProductService is given below
export class ProductService extends ProductRepositoryManager{
static $inject = ["$q"];
constructor($q: ng.IQService, repoType: string){
super(repoType, $q);
}
}